Red circle on the skin but not ringworm: Other causes - Medical News Today
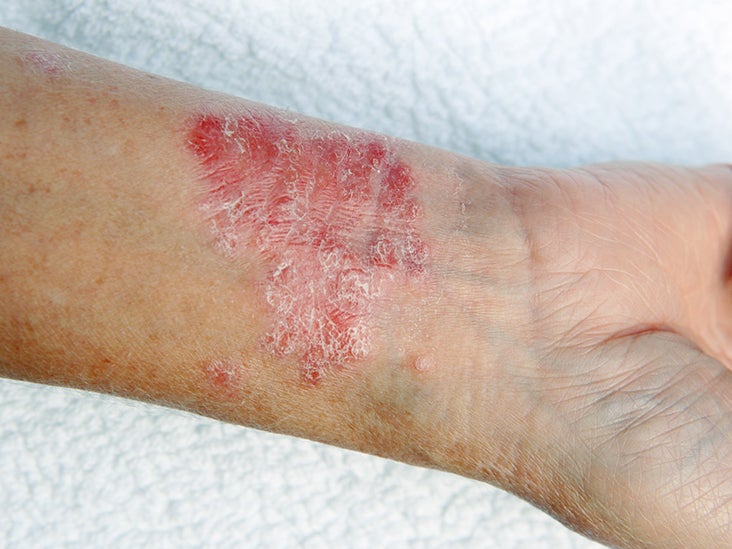
Ringworm is characterized by scaly red patches, or "rings," on the skin. But many other skin conditions can cause the same symptom.
This article looks at skin conditions that resemble ringworm and the range of treatments and strategies for prevention.
Pityriasis rosea is a common, mild skin rash that usually lasts for 6–8 weeks.
It causes a scaly pink patch, about 2–10 centimeters (cm) in diameter, to form on the skin. When the rash is smaller, it can be mistaken for ringworm, and it usually develops on the torso or neck.
The rash is not painful but may be itchy. In dark-skinned people, it may appear grey, dark brown, or black. In light-skinned people, it may appear pink or red.
A viral infection, such as herpes, is likely the cause of pityriasis rosea. But it is not contagious and cannot spread through physical contact.
Learn more about pityriasis rosea here.
Contact dermatitis is a type of eczema that forms in response to a substance irritating the skin.
A person with contact dermatitis may be having an allergic reaction to certain metals, such as nickel or cobalt, ingredients in cosmetics or soaps, or materials such as latex.
The term "contact dermatitis" is also used to describe skin irritation such as diaper rash or cracked skin after excessive hand washing.
Because contact dermatitis can cause patches of thickened, scaly skin to form, it can be confused with ringworm. On lighter skin, the patches may be red, while on darker skin they may be dark brown, purple, or gray.
Learn more about contact dermatitis here.
Nummular eczema, also known as nummular dermatitis or discoid eczema, is an inflammatory condition that causes coin-shaped patches of itchy, swollen skin to appear. This can occur anywhere on the body.
The patches tend to measure 1–4 inches, though they may be smaller, and they can be pink, red, or brown. The itching or burning sensations may be worse at night, and the patches may leak fluid or crust over.
It is not clear what causes nummular eczema, but a sensitivity to a certain metal, chemical, or medicine may be a trigger. Also, the symptoms may be worse in humid climates or cold, dry climates.
Learn more about the differences between nummular eczema and ringworm here.
Granuloma annulare is a rare, chronic skin disorder. It is not contagious or cancerous.
It causes patches of skin to form with a distinctive border of small, firm bumps. The patches may be 1–5 cm in diameter and appear on the legs and arms, and the color of the bumps may be yellow, red, pink, or purple.
The rash is not usually painful, but it is sometimes itchy.
The most common type is localized granuloma annulare. It affects children and young adults and usually goes away without treatment.
Experts are not sure exactly what causes granuloma annulare, but it may involve:
Psoriasis is a common long-term skin condition that develops when the body produces skin cells too quickly. The cells pile up, forming visible patches on the skin's surface.
The patches can:
- be silvery
- occur with other color changes
- be flaky or crusty
- be itchy or sore
- cause a burning sensation
- appear anywhere on the body — but most commonly on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back
Experts believe that psoriasis stems from problems with the immune system that cause the body to attack healthy skin cells.
It is not contagious, and it can run in families but is not always hereditary. The following factors can trigger psoriasis:
- hormonal changes
- excessive alcohol intake
- stress
- injuries to the skin, including insect bites and sunburn
- strep throat
- certain medicines, such as anti-inflammatory or high blood pressure medications
Learn more about the differences between psoriasis and ringworm here.
Lyme disease is a bacterial infection caused by a bite from a black-legged tick.
People with Lyme disease tend to develop a circular bull's-eye rash around the bite mark. On lighter skin, it may appear red or purple. On darker skin, it may appear dark brown or black.
The rash may be itchy or painful and occur with a burning sensation. It may be smooth or have a scaly or crusty outer border.
In about half of cases, Lyme disease also causes flu-like symptoms, such as a fever, muscle aches, and fatigue.
Learn more about Lyme disease here.
The right treatment approach for a red, circular rash depends on the cause, and an accurate diagnosis is key.
Taking into account the severity of the rash and any other symptoms, a person may benefit from a combination of the following treatments and home care strategies:
Avoiding the cause
Conditions such as contact dermatitis, nummular eczema, and psoriasis can occur or flare up in response to triggers. Identifying and avoiding specific triggers can help keep the symptoms at bay.
Emollients
Emollients are moisturizing treatments that help soothe and hydrate the skin, reduce itchiness, and prevent inflammation.
They come as lotions, sprays, or soap substitutes. In most cases, a person can purchase emollients from a pharmacy without a prescription.
Topical treatments and drugs
Professional treatment often starts with a medicated ointment or cream, which may contain corticosteroids or antibiotics.
A doctor may also recommend corticosteroid injections or tablets, oral antibiotics, or oral antihistamines.
However, for Lyme disease, antibiotic tablets or injections are the first-line treatment.
For psoriasis, the wide range of medicated creams includes:
- dithranol or vitamin D analog creams to slow skin cell production
- calcineurin inhibitor creams to suppress the immune system
- coal tar, a thick, heavy oil, to reduce itchiness and inflammation
Other therapies
Some forms of light therapy, such as ultraviolet light therapy, may help with granuloma annulare, nummular eczema, psoriasis, and pityriasis rosea.
Immunosuppressant therapy can also help with nummular eczema and contact dermatitis.
Cryotherapy, which involves freezing areas of skin with liquid nitrogen, can help control granuloma annulare.
If an unexplained rash lasts longer than a few weeks, see a doctor, such as a dermatologist.
It is especially important to receive professional care if the rash:
- is all over the body
- is painful
- seems to be infected
- begins to blister, especially near the eyes, inside the mouth, or near the genitals
- occurs with any fatigue or joint pain
The American Academy of Dermatology recommend receiving emergency care if a rash:
- accompanies a fever
- accompanies difficulty breathing
- appeared suddenly and is spreading quickly
Rashes that are circular and scaly do not always indicate ringworm. They can result from several common health issues, some of which are more serious than others.
A variety of treatments are available, and the best approach depends on the rash's cause and severity.
Anyone with an unexplained rash should receive a professional diagnosis. If a rash has appeared and spread very quickly, or if it occurs with a fever or difficulty breathing, contact emergency services.


Comments
Post a Comment